Heat and energy transport phenomena
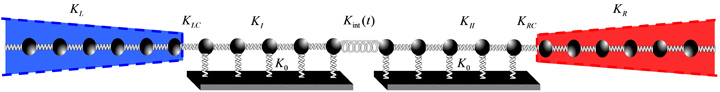
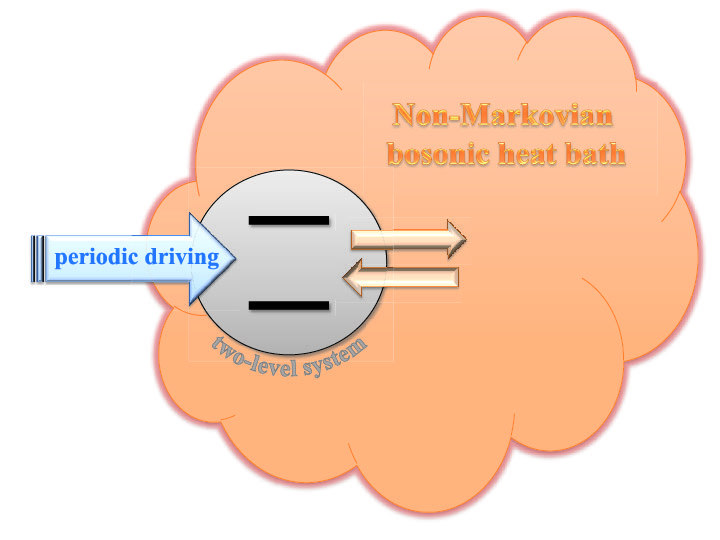
Time dependent systems
We study energy transport phenomena in low dimensional systems subject to time dependent fields and inmersed in complex environments.
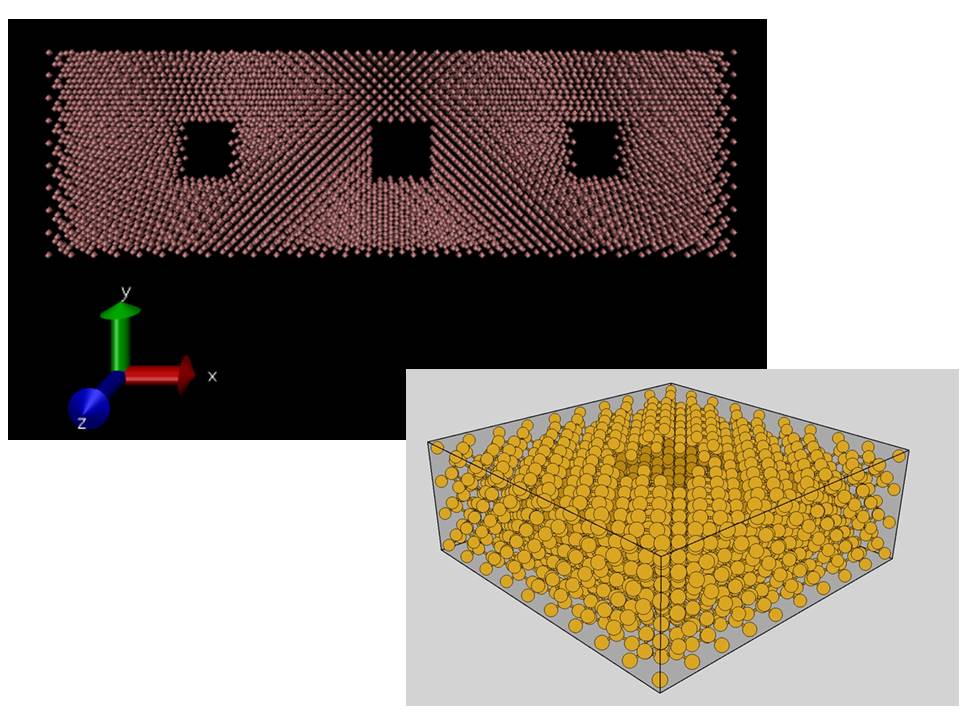
Phononics. Heat transport in micro/nanostructured materials.
We study the heat transport in Silicon micro/nanostructures. These low dimensional nanomaterials have a big relevance due to their technological applications. They can be designed to transport energy in a control way according to the necessity.

Nanofluids and microfluidics for thermal management.
Transport phenomena in soft and active matter

Flexible filaments in viscous media. Aplications to biophysics and engineering.
Dentro de las células eucariotas existen estructuras cuasi unidimensionales como microtúbulos, filamentos intermedios y de actina. Los desplazamientos y ondulaciones observados en estos filamentos no se entienden cabalmente, tanto por el origen de las fuerzas que los provocan, como por su función biológica. Dentro de este plan se hará un estudio de las propiedades mecánicas de filamentos intracelulares, sometidos a fuerzas activas y térmicas, así como el estudio de experimentos de varillas inmersas en medios viscosos y viscoelásticos, que serían un modelo macroscópico plausible de las estructuras intracelulares.
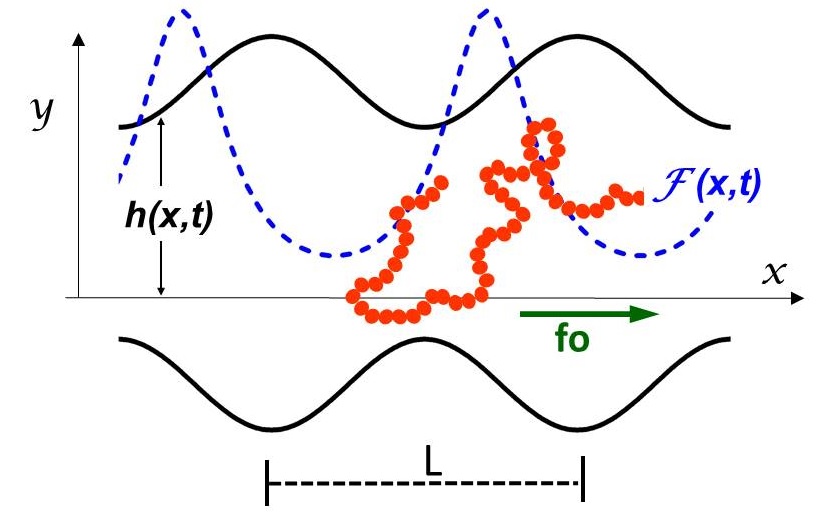
Transport phenomena in soft matter under confinement.
We study the transport properties of colloids and polymers inmersed in fluids confined in micro/nanochannels. These confinements produce entropic barriers that affect the dynamics and energetics of the particles. In particular, we are focused on the role played on trasport by the geometrical characteristics of the channels, the characteristics of the soft particles and of the fluid or solvent.

Transport phenomena in active matter.
Transport phenomena in large scale complex systems
Computing, Simulation and Optimization to improve river flood prediction. High performance computing to offer solutions to problems of social impact.
The simulation of real systems are lines of development and research highly benefited by the advances of high performance computing (HPC) and parallel programming. HPC has become a fundamental and essential technology for computer simulations. Modelling and computational simulation provide powerful tools which enable an efficient and reliable flood event forecasting. Simulation and optimization methods and techniques requires the capacity of HPC systems when efficient methodologies are implemented to provide improvements in the prediction quality of such simulators.
In this research line, we aim to provide more efficient and more reliable solutions to calibrate the simulation of wave translation in river channels. We use optimization via simulation and HPC technologies to generate and implement automatic calibration methodologies. We propose add an improvement process on the classical computer model output to provide more accurate values of water levels.
